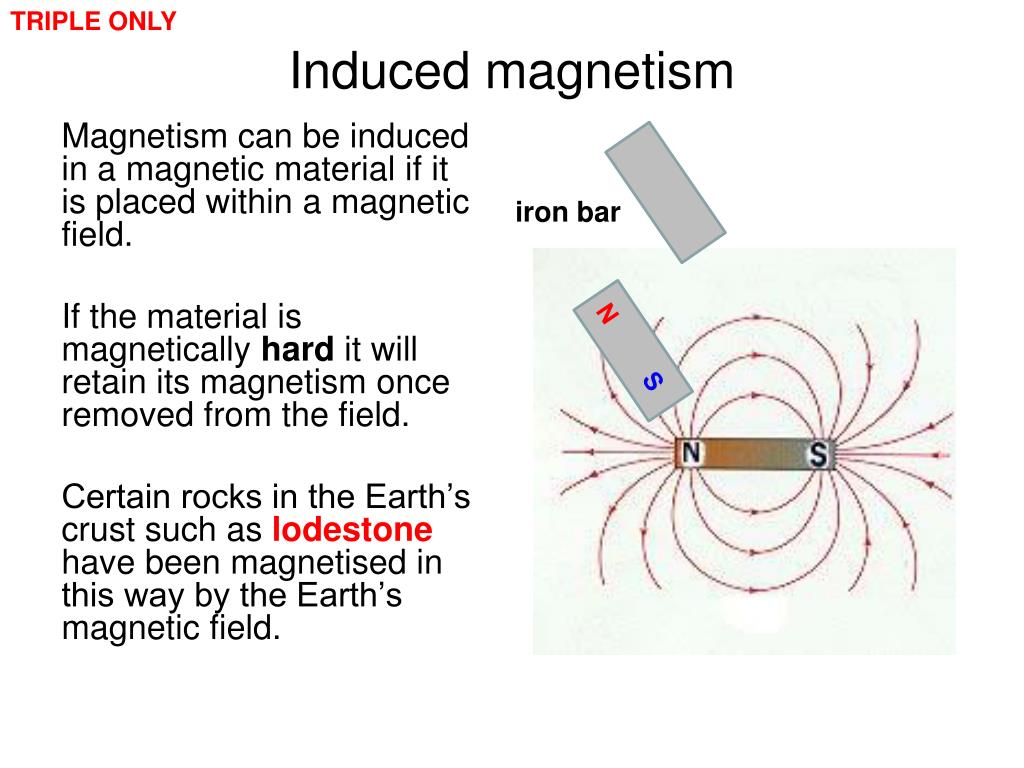
Magnetic Chemistry Explained . anything that is magnetic, like a bar magnet or a loop of electric current, has a magnetic moment. The north pole points toward earth's north magnetic field. the resultant combination of the spin and orbital magnetic moments of the constituent atoms of a material gives rise to the observed magnetic. magnetism is a physical phenomenon by which a substance is attracted or repelled by a magnetic field. the magnetic form of a substance can be determined by examining its electron configuration: A magnet has an invisible magnetic field surrounding it and two ends called poles. magnetism is the force exerted by magnets when they attract or repel each other. The south pole points toward the earth's south magnetic field. diamagnetism, paramagnetism, and ferromagnetism are the three main types of magnetism seen in. magnetism arises from the electromagnetic force of a moving electric charge. A magnetic moment is a. The two sources of magnetism. Magnetism is caused by the motion of electric.
from www.slideserve.com
The south pole points toward the earth's south magnetic field. anything that is magnetic, like a bar magnet or a loop of electric current, has a magnetic moment. A magnetic moment is a. The two sources of magnetism. Magnetism is caused by the motion of electric. The north pole points toward earth's north magnetic field. magnetism arises from the electromagnetic force of a moving electric charge. magnetism is the force exerted by magnets when they attract or repel each other. the magnetic form of a substance can be determined by examining its electron configuration: diamagnetism, paramagnetism, and ferromagnetism are the three main types of magnetism seen in.
PPT EDEXCEL IGCSE / CERTIFICATE IN PHYSICS 61 and
Magnetic Chemistry Explained The south pole points toward the earth's south magnetic field. The two sources of magnetism. magnetism is the force exerted by magnets when they attract or repel each other. the resultant combination of the spin and orbital magnetic moments of the constituent atoms of a material gives rise to the observed magnetic. the magnetic form of a substance can be determined by examining its electron configuration: diamagnetism, paramagnetism, and ferromagnetism are the three main types of magnetism seen in. A magnet has an invisible magnetic field surrounding it and two ends called poles. anything that is magnetic, like a bar magnet or a loop of electric current, has a magnetic moment. magnetism is a physical phenomenon by which a substance is attracted or repelled by a magnetic field. Magnetism is caused by the motion of electric. A magnetic moment is a. The south pole points toward the earth's south magnetic field. The north pole points toward earth's north magnetic field. magnetism arises from the electromagnetic force of a moving electric charge.
From msestudent.com
Materials Types of Applications, and Origin of Magnetic Chemistry Explained A magnetic moment is a. magnetism is a physical phenomenon by which a substance is attracted or repelled by a magnetic field. anything that is magnetic, like a bar magnet or a loop of electric current, has a magnetic moment. the magnetic form of a substance can be determined by examining its electron configuration: A magnet has. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From www.eurekalert.org
Molecular [IMAGE] EurekAlert! Science News Releases Magnetic Chemistry Explained The south pole points toward the earth's south magnetic field. magnetism arises from the electromagnetic force of a moving electric charge. anything that is magnetic, like a bar magnet or a loop of electric current, has a magnetic moment. the magnetic form of a substance can be determined by examining its electron configuration: A magnet has an. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2043253 Magnetic Chemistry Explained Magnetism is caused by the motion of electric. the resultant combination of the spin and orbital magnetic moments of the constituent atoms of a material gives rise to the observed magnetic. anything that is magnetic, like a bar magnet or a loop of electric current, has a magnetic moment. magnetism is the force exerted by magnets when. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From www.doubtnut.com
Explain with the help of a labelled diagram the distribution of Magnetic Chemistry Explained magnetism arises from the electromagnetic force of a moving electric charge. The two sources of magnetism. A magnet has an invisible magnetic field surrounding it and two ends called poles. magnetism is a physical phenomenon by which a substance is attracted or repelled by a magnetic field. the resultant combination of the spin and orbital magnetic moments. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT EDEXCEL IGCSE / CERTIFICATE IN PHYSICS 61 and Magnetic Chemistry Explained the resultant combination of the spin and orbital magnetic moments of the constituent atoms of a material gives rise to the observed magnetic. magnetism is the force exerted by magnets when they attract or repel each other. anything that is magnetic, like a bar magnet or a loop of electric current, has a magnetic moment. A magnetic. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From learning-center.homesciencetools.com
& science lesson plan Magnetic Chemistry Explained A magnetic moment is a. magnetism is a physical phenomenon by which a substance is attracted or repelled by a magnetic field. magnetism arises from the electromagnetic force of a moving electric charge. the resultant combination of the spin and orbital magnetic moments of the constituent atoms of a material gives rise to the observed magnetic. . Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From www.pinterest.com
Metallurgy Separation method Chemistry notes, Method, Chemistry Magnetic Chemistry Explained diamagnetism, paramagnetism, and ferromagnetism are the three main types of magnetism seen in. magnetism is a physical phenomenon by which a substance is attracted or repelled by a magnetic field. magnetism is the force exerted by magnets when they attract or repel each other. A magnet has an invisible magnetic field surrounding it and two ends called. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From www.youtube.com
Domains Explained with a Demonstration of a Pin Magnetic Chemistry Explained diamagnetism, paramagnetism, and ferromagnetism are the three main types of magnetism seen in. magnetism is a physical phenomenon by which a substance is attracted or repelled by a magnetic field. The south pole points toward the earth's south magnetic field. A magnetic moment is a. A magnet has an invisible magnetic field surrounding it and two ends called. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From sciencestruck.com
Here's a Simple Explanation of How Work Science Struck Magnetic Chemistry Explained anything that is magnetic, like a bar magnet or a loop of electric current, has a magnetic moment. the magnetic form of a substance can be determined by examining its electron configuration: A magnetic moment is a. Magnetism is caused by the motion of electric. A magnet has an invisible magnetic field surrounding it and two ends called. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2043253 Magnetic Chemistry Explained Magnetism is caused by the motion of electric. diamagnetism, paramagnetism, and ferromagnetism are the three main types of magnetism seen in. anything that is magnetic, like a bar magnet or a loop of electric current, has a magnetic moment. A magnet has an invisible magnetic field surrounding it and two ends called poles. The south pole points toward. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From www.cbsedigitaleducation.com
and Matter Class 12 Notes Definition,Facts,Types Magnetic Chemistry Explained A magnetic moment is a. the resultant combination of the spin and orbital magnetic moments of the constituent atoms of a material gives rise to the observed magnetic. magnetism is the force exerted by magnets when they attract or repel each other. A magnet has an invisible magnetic field surrounding it and two ends called poles. magnetism. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From www.thesciencehive.co.uk
(GCSE) — the science sauce Magnetic Chemistry Explained diamagnetism, paramagnetism, and ferromagnetism are the three main types of magnetism seen in. The two sources of magnetism. The north pole points toward earth's north magnetic field. Magnetism is caused by the motion of electric. anything that is magnetic, like a bar magnet or a loop of electric current, has a magnetic moment. the resultant combination of. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From www.worksheetsplanet.com
What is a Definition of Magnetic Chemistry Explained magnetism arises from the electromagnetic force of a moving electric charge. The north pole points toward earth's north magnetic field. magnetism is a physical phenomenon by which a substance is attracted or repelled by a magnetic field. magnetism is the force exerted by magnets when they attract or repel each other. anything that is magnetic, like. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From stoplearn.com
and its properties and Types, field and Magnetic Chemistry Explained The north pole points toward earth's north magnetic field. the resultant combination of the spin and orbital magnetic moments of the constituent atoms of a material gives rise to the observed magnetic. A magnet has an invisible magnetic field surrounding it and two ends called poles. diamagnetism, paramagnetism, and ferromagnetism are the three main types of magnetism seen. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT CHAPTER 20 PROPERTIES PowerPoint Presentation, free Magnetic Chemistry Explained anything that is magnetic, like a bar magnet or a loop of electric current, has a magnetic moment. magnetism is a physical phenomenon by which a substance is attracted or repelled by a magnetic field. magnetism is the force exerted by magnets when they attract or repel each other. The two sources of magnetism. the magnetic. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From exoezykzu.blob.core.windows.net
What Are Two Common Materials That Are at Keith Wallace blog Magnetic Chemistry Explained diamagnetism, paramagnetism, and ferromagnetism are the three main types of magnetism seen in. The north pole points toward earth's north magnetic field. magnetism is the force exerted by magnets when they attract or repel each other. A magnet has an invisible magnetic field surrounding it and two ends called poles. the resultant combination of the spin and. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From www.youtube.com
Earth's Field Explained Terrestrial Science Magnetic Chemistry Explained magnetism is the force exerted by magnets when they attract or repel each other. Magnetism is caused by the motion of electric. diamagnetism, paramagnetism, and ferromagnetism are the three main types of magnetism seen in. magnetism is a physical phenomenon by which a substance is attracted or repelled by a magnetic field. A magnetic moment is a.. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.
From studyfercequeekspk.z21.web.core.windows.net
Easy Science Experiments Using Magnetic Chemistry Explained magnetism is the force exerted by magnets when they attract or repel each other. magnetism is a physical phenomenon by which a substance is attracted or repelled by a magnetic field. The south pole points toward the earth's south magnetic field. anything that is magnetic, like a bar magnet or a loop of electric current, has a. Magnetic Chemistry Explained.